- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- haitian_creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- scottish-gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu

авг . 13, 2025 03:00 Back to list
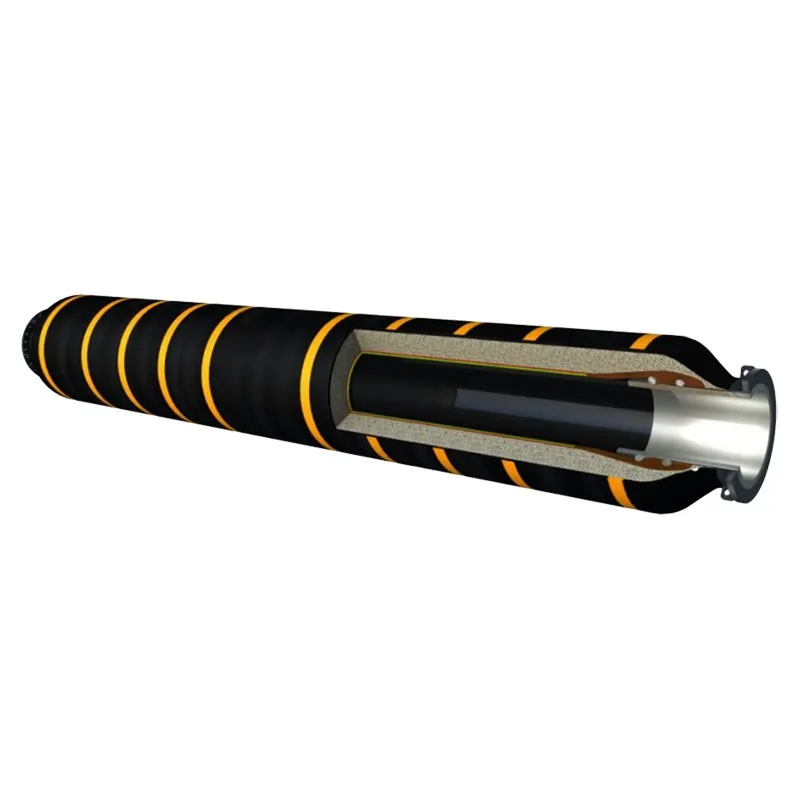
Self-Floating Dredging Hoses for Marine & Offshore Use
Navigating the Waters: Trends and Advancements in Floating Dredging Technology
The global dredging industry is experiencing significant transformation, driven by infrastructure development, port expansion, land reclamation projects, and environmental remediation initiatives. Central to these operations is the efficient and reliable transport of dredged material, a task critically dependent on robust pipeline systems. Among these, the floating dredging hose stands out as a pivotal component, offering unmatched flexibility and operational stability. Recent trends indicate a strong demand for hoses with enhanced durability, superior abrasion resistance, and improved buoyancy, capable of withstanding harsh marine environments and abrasive slurries. Innovations in material science, particularly in rubber compounding and reinforcement, are enabling longer service life and reduced maintenance downtime, directly contributing to the economic viability of large-scale dredging projects worldwide. This evolution reflects the industry's commitment to efficiency, sustainability, and operational excellence in challenging maritime applications.

Technological advancements are not only focused on raw material improvements but also on intelligent monitoring systems integrated into floating hose segments. These systems, often incorporating sensors, can provide real-time data on pressure, flow, and even hose integrity, enabling predictive maintenance and preventing costly failures. The shift towards more sustainable dredging practices also influences hose design, with manufacturers exploring environmentally friendly materials and production processes. The demand for specialized applications, such as high-pressure dredging or the transport of highly corrosive substances, further propels the need for tailor-made solutions. These developments underscore the critical role of advanced engineering and material science in shaping the future of hydraulic dredging.
Deconstructing the Floating Dredging Hose: Design and Technical Parameters
A floating dredging hose is a specialized flexible pipeline engineered to transport abrasive slurries, sand, gravel, and other dredged materials over water. Unlike conventional submerged pipelines or rigid steel pipes, these hoses incorporate integral buoyancy layers, allowing them to float on the water surface. This self-floating capability is crucial for maintaining the pipeline's position and flexibility, adapting to wave action and vessel movements without requiring external pontoons. Key design elements include an inner wear-resistant lining, a robust textile or steel wire reinforcement layer, and an outer weather-resistant cover. The integral buoyancy material, typically closed-cell foam, is strategically placed between the reinforcement and the outer cover, ensuring optimal floatation and stability.
Critical technical parameters define the performance envelope of a floating dredging hose. These include the nominal bore (ID), working pressure (WP), burst pressure (BP), minimum bending radius (MBR), and specific gravity of the conveyed medium. For instance, a common dredging hose might feature an ID ranging from 150mm to 1200mm, with working pressures typically between 10 bar and 25 bar. The abrasion resistance of the inner liner is often measured in terms of material loss after a specific number of cycles, indicating its longevity when exposed to abrasive media. Furthermore, the overall weight per meter, including the integral floats, is essential for calculating installation dynamics and buoyancy characteristics. Understanding these specifications is paramount for selecting the right hose for specific project requirements, ensuring operational efficiency and safety.
The Precision of Production: Manufacturing a Floating Dredging Hose
The manufacturing of a floating dredging hose is a highly specialized process, combining advanced material science with precise engineering techniques. The process typically begins with the extrusion of the inner liner, which is formulated from highly abrasion-resistant synthetic rubber compounds, often incorporating high-grade natural rubber or specially blended elastomers to withstand continuous slurry flow. This liner is crucial for preventing wear and extending the hose's service life, particularly when handling materials like sharp sand or crushed rock.

Following the inner liner, multiple layers of high-tensile textile fabric or steel wire reinforcement are spirally wound around the liner. This reinforcement provides the structural integrity and pressure-bearing capability of the hose, designed to meet specific working pressure requirements (e.g., up to 25 bar for heavy-duty applications). A critical step involves the integration of closed-cell foam buoyancy layers, which are precisely applied to achieve the desired self-floating characteristics. This foam is designed to resist water absorption and maintain buoyancy even if punctured. Finally, an outer cover, made from weather-resistant synthetic rubber, is applied to protect the internal components from UV radiation, ozone, abrasion, and marine elements. The entire assembly then undergoes a vulcanization process under controlled temperature and pressure, bonding all layers into a monolithic structure. Each hose undergoes rigorous testing, including hydrostatic pressure tests (e.g., 1.5 times the working pressure), vacuum tests, and visual inspections to conform to international standards such as ISO 1823:2015 for rubber hoses or client-specific specifications like IACS or OCIMF for marine applications. These stringent quality control measures ensure a product lifespan typically ranging from 5 to 10 years, depending on application severity.
Unlocking Operational Efficiency: Technical Advantages of Floating Dredging Hose
The inherent design of the floating dredging hose confers several significant technical advantages over traditional dredging pipelines, directly translating into enhanced operational efficiency and cost savings. Firstly, its self-floating nature eliminates the need for external pontoons, significantly reducing installation time, logistics complexity, and capital expenditure associated with auxiliary floating devices. This simplifies pipeline layout and relocation, making operations more agile and adaptable to changing site conditions, particularly in dynamic marine environments or along winding waterways. The reduced ancillary equipment also translates to lower fuel consumption for support vessels and a smaller carbon footprint, contributing to energy efficiency.
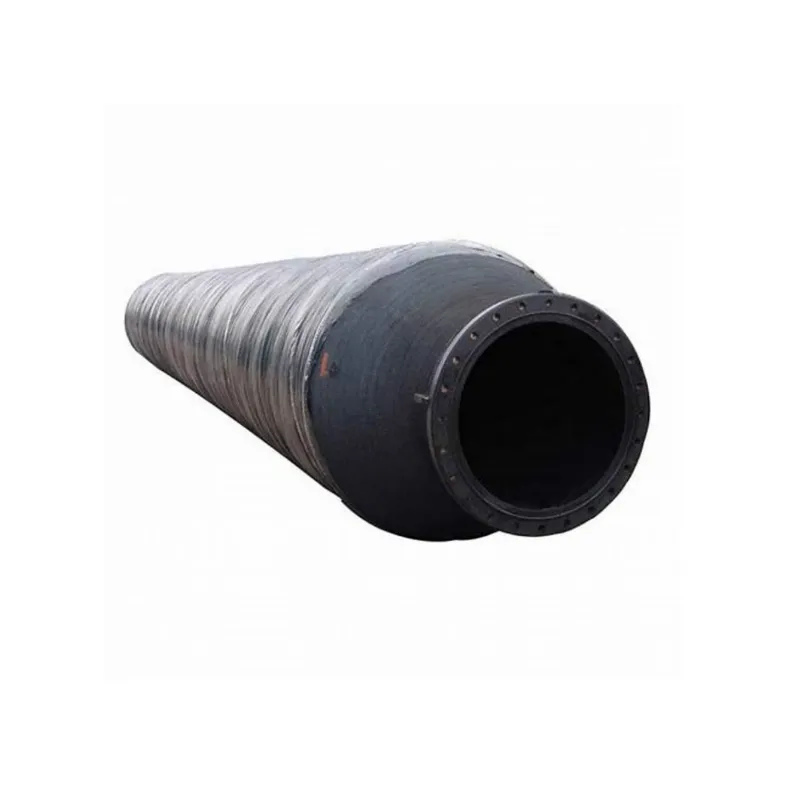

Secondly, the exceptional flexibility of a floating dredging hose allows it to absorb shocks, vibrations, and movements caused by waves, tides, and vessel maneuvers. This flexibility minimizes stress on the entire pipeline system and connecting equipment, preventing premature wear and fatigue failures common in rigid piping systems. The superior abrasion resistance of the inner liner, specifically engineered for highly abrasive slurry transport, ensures prolonged operational life even under continuous heavy-duty use. This corrosion-resistant and fatigue-resistant design, coupled with ease of maintenance, drastically reduces downtime and replacement costs, making it a cost-effective solution for long-term dredging projects across industries like port construction, mining, and environmental restoration. The combination of robustness, flexibility, and inherent buoyancy positions these hoses as an indispensable asset for modern dredging operations.
Versatile Applications: Where Floating Dredging Hose Excels
The robust design and inherent flexibility of the floating dredging hose make it indispensable across a multitude of challenging applications in various industries. In the Marine and Offshore sector, these hoses are vital for port and harbor deepening, channel maintenance, and land reclamation projects, allowing dredgers to efficiently transport large volumes of sand, silt, and clay over water to deposition sites. Their ability to handle the dynamic forces of the open sea, including wave action and strong currents, makes them preferred for `floating hose offshore` operations and `marine floating hoses` systems.
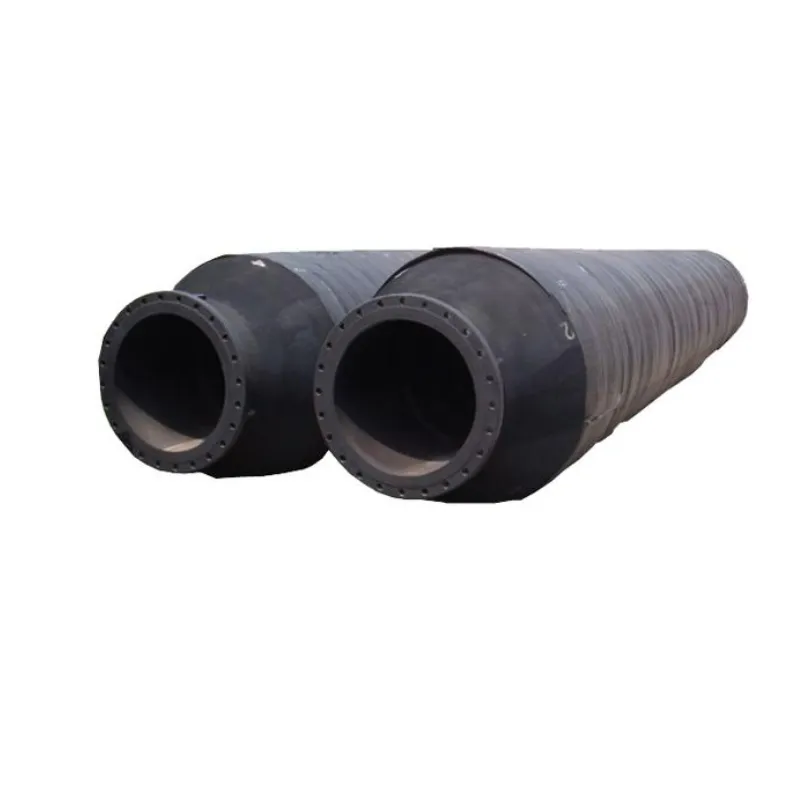

Beyond traditional dredging, `floating dredging pipe` and `floating rubber hose` solutions are critical in Mining for tailing removal and transport of mineral slurries from onshore processing plants to offshore discharge points. Their resistance to abrasive materials and chemical inertness (when specified for particular media) ensures reliable performance. In Environmental Remediation, they are employed for sediment removal from contaminated lakes, rivers, and reservoirs, facilitating the restoration of aquatic ecosystems. Furthermore, specific variants like `floating oil hose` or `submarine hoses` (designed for submerged applications) cater to specialized needs in oil and gas, for example, transferring crude oil or refined products from offshore production platforms to tankers or shore facilities. The adaptability of these hoses extends to demanding industrial processes like power plant ash disposal and various `water supply and drainage` projects where flexible, large-bore piping is required. Their broad applicability underscores their significance in complex fluid and solid transport operations.
Performance at a Glance: Key Specifications of Floating Dredging Hose
Selecting the appropriate floating dredging hose necessitates a thorough understanding of its technical specifications. Below is a detailed table outlining typical parameters for high-performance floating dredging hoses. These values represent the general capabilities, and specific project requirements might necessitate custom designs to meet unique pressure, abrasion, or environmental demands. It is crucial for project managers and engineers to assess these parameters against the anticipated operational conditions, including the type of dredged material, flow rate, operating temperature, and external environmental factors, to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
These specifications are foundational for engineers designing dredging systems, influencing pump selection, pipeline layout, and overall project safety. The durability of `self floating hose` is directly correlated with the quality of its inner liner and the strength of its reinforcement, which are critical for maintaining operational integrity in demanding conditions.
Tailored Solutions: Customizing Your Floating Dredging Hose
While standard floating dredging hose models offer broad applicability, many complex dredging projects demand highly customized solutions. Leading manufacturers understand that factors such as the specific gravity of the dredged material, the presence of hydrocarbons, extreme temperatures, or unique coupling requirements necessitate tailor-made hose designs. Customization options extend to the choice of inner liner material, where specialized compounds can be engineered for enhanced resistance to chemicals or exceptionally abrasive media. For instance, scenarios involving aggressive chemical slurries might call for EPDM or Hypalon liners, while ultra-high abrasion environments could benefit from ceramic-reinforced rubber or advanced polyurethane composites.
Furthermore, the reinforcement layers can be adjusted to achieve higher working pressures or increased flexibility, balancing strength with maneuverability. Buoyancy levels can also be fine-tuned to ensure optimal floating characteristics in varying water densities or to accommodate specific installation methods. End connections are another key area for customization, with options ranging from fixed or swivel flanges compliant with international standards (e.g., ANSI, DIN) to specialized quick-release couplings for rapid deployment and retrieval. Manufacturers work closely with clients to conduct detailed engineering analyses, including finite element analysis (FEA) for stress distribution and wear prediction, ensuring the final `floating hose` solution precisely matches the project's unique operational demands and environmental constraints, maximizing efficiency and minimizing risks.
Success Stories: Floating Dredging Hose in Action
The proven efficacy of floating dredging hose solutions is best exemplified through real-world applications. Consider a recent major port expansion project in Southeast Asia, where over 5 kilometers of 800mm ID `floating rubber hose` were deployed for land reclamation. The project involved transporting highly abrasive sand and shell fragments over fluctuating tidal waters. The chosen hoses, equipped with a proprietary high-abrasion liner and integral buoyancy, maintained consistent flow rates and exhibited minimal wear over the project's 18-month duration, significantly contributing to the project's ahead-of-schedule completion. This contrasts sharply with previous projects where traditional steel pipelines led to frequent blockages and extensive maintenance, causing costly delays.
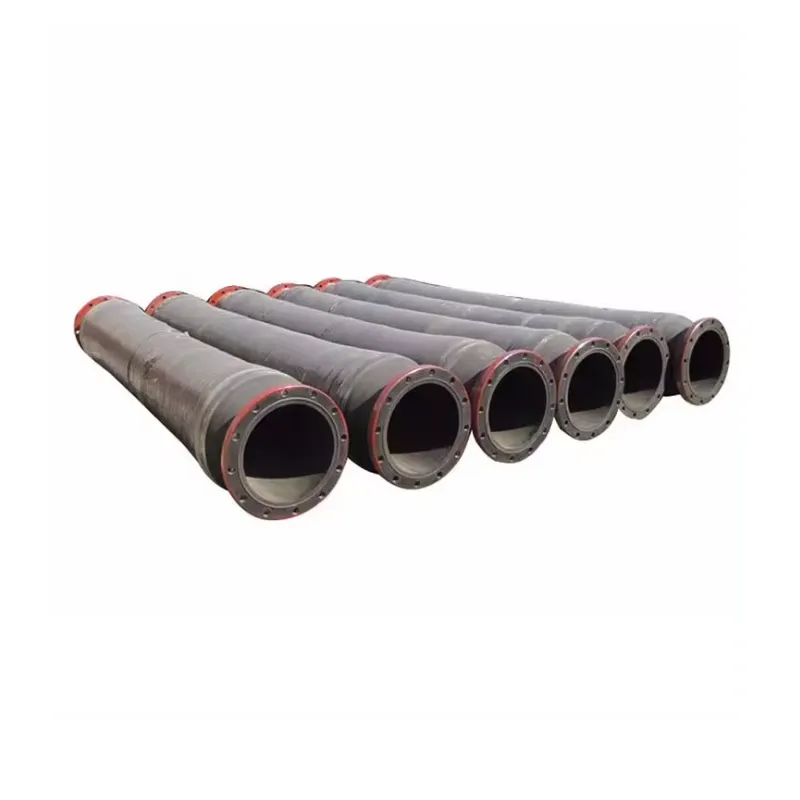

Another compelling case involved an environmental remediation effort in a large contaminated lake in North America. Here, a series of 450mm ID `self floating hose` segments were utilized to remove decades of accumulated sludge and sediment. The hose's flexibility was critical for navigating complex lakebed topography and avoiding sensitive ecological zones. The integral floats ensured the pipeline remained on the surface, preventing disturbance to the fragile underwater environment while simplifying deployment and repositioning. Client feedback highlighted the ease of installation and the minimal environmental footprint as key advantages, reinforcing the value proposition of these specialized `floating hose` systems in sensitive applications. These instances underscore the reliability and adaptability of advanced `floating dredging pipe` technology in diverse, demanding scenarios.
Navigating the Market: Manufacturer Comparison Considerations
When sourcing a floating dredging hose, discerning buyers in the B2B sector must evaluate manufacturers based on a comprehensive set of criteria beyond just initial cost. A critical factor is the manufacturer's material expertise and engineering capabilities. Leading providers invest heavily in R&D, developing proprietary rubber compounds for superior abrasion resistance, UV stability, and chemical compatibility, ensuring the longevity of their `floating hose` products in harsh marine and industrial settings. Their ability to conduct advanced simulations and provide detailed performance data is a testament to their technical prowess.
Another crucial aspect is adherence to international quality standards and certifications. Manufacturers compliant with ISO 9001 for quality management and ISO 1823 for rubber hose specifications demonstrate a commitment to consistent product quality and safety. Furthermore, companies with extensive service history and a track record of successful project deliveries, especially those providing comprehensive after-sales support, installation guidance, and troubleshooting, often prove to be more reliable partners. Customization capabilities are equally important, as not all projects fit standard specifications. A manufacturer capable of engineering bespoke `floating dredging pipe` solutions for unique pressure ratings, specialized end fittings, or unusual operating temperatures adds significant value. Finally, evaluating their supply chain efficiency and delivery lead times can be pivotal for project schedules, especially for large-scale global dredging operations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Floating Dredging Hose
Q1: What defines the lifespan of a floating dredging hose?
The lifespan of a floating dredging hose is primarily determined by the abrasiveness of the material being transported, the frequency of use, operational pressure, and proper handling/maintenance. High-quality hoses with superior abrasion-resistant liners can last typically between 5 to 10 years, sometimes longer with intermittent use and ideal conditions. Regular inspection for wear and tear, especially of the inner lining and outer cover, is crucial for maximizing service life.
Q2: Can floating dredging hose be repaired, or does it always need replacement?
Minor external damage to the outer cover or buoyancy layer of a `floating rubber hose` can often be repaired using specialized patching kits or vulcanization techniques, extending the hose's operational life. However, severe damage to the internal wear liner or reinforcement layers typically necessitates replacement of the hose segment to maintain integrity and prevent catastrophic failure. Consult the manufacturer's guidelines for specific repair protocols.
Q3: How does integral buoyancy in a `self floating hose` compare to external pontoons?
Integral buoyancy, where floatation is built into the hose wall, offers superior stability and ease of deployment compared to external pontoons. It reduces overall pipeline diameter, simplifies handling, minimizes snagging risks, and requires less deck space for transport and storage. External pontoons, while offering flexibility for conventional pipes, introduce additional connection points, potential for detachment, and higher logistical demands during installation and relocation.
Q4: Are floating dredging hose products suitable for both suction and discharge applications?
Many `floating hose` designs, especially those with reinforced wire helix structures, are engineered for both suction and discharge applications. Suction hoses require robust construction to prevent collapse under vacuum, while discharge hoses need high burst strength to withstand internal pressure. It's crucial to specify the intended application (suction, discharge, or both) when ordering to ensure the correct internal reinforcement is integrated.
Commitment to Excellence: Quality Assurance and Customer Support
For B2B clients, the reliability of a floating dredging hose extends beyond its immediate technical specifications to encompass the manufacturer's commitment to quality assurance and comprehensive customer support. Reputable manufacturers adhere to stringent quality control protocols at every stage of the production process, from raw material inspection to final product testing. This includes rigorous hydrostatic pressure testing, dimensional checks, and material certifications, ensuring compliance with international standards such as ISO 9001 and specific marine classifications like IACS where applicable. Certificates of conformity and test reports are typically provided with each shipment, offering full transparency and traceability for every `floating hose` delivered.
Furthermore, a strong emphasis on customer support is paramount. This includes expert technical consultation during the project planning phase, assisting clients in selecting the most suitable `floating dredging pipe` for their specific needs. Efficient order processing and clear communication regarding manufacturing lead times and delivery schedules are standard, with typical delivery periods ranging from 4 to 8 weeks for standard orders, depending on customization. Most importantly, a robust warranty commitment, often extending for 12 to 24 months from delivery or installation, provides critical peace of mind. This commitment is often complemented by readily available after-sales support, including spare parts, on-site technical assistance, and guidance on installation and maintenance best practices, ensuring optimal performance and extended service life of the floating dredging hose throughout its operational tenure.
References
- ISO 1823:2015, Rubber hoses and hose assemblies for dredging and sand suction applications – Specification. International Organization for Standardization.
- Prak, M. (2018). Dredging Technology: Principles and Applications. Delft University of Technology.
- United States Army Corps of Engineers. (2010). Engineering and Design - Dredging and Dredged Material Disposal. EM 1110-2-5025.
- International Association of Classification Societies (IACS). (2020). Unified Requirements for Dredging Appliances.
- The World Organisation of Dredging Associations (WODA). (2023). Industry Best Practices Guidelines.
This is the first article
Latest News
Steel Wire Reinforced Hydraulic Hose SAE 100 R1 / EN853 1SN S
NewsOct.17,2024
Two Layers Steel Wire Reinforced Hydraulic Hose SAE 100 R2 / EN853 2SN
NewsSep.03,2024
Textile Braid Reinforced Hydraulic Hose SAE100 R3+R6
NewsSep.03,2024
Textile Reinforced Hydraulic oil Suction Hose with embedded Steel Wire SAE 100 R4
NewsSep.03,2024
Single Wire Braid and Textile Covered Hydraulic Hose SAE 100 R5
NewsSep.03,2024
High Pressure Thermoplastic Hydraulic Hose SAE 100 R7 / EN855 R7 - SAE 100 R8 / EN855 R8
NewsSep.03,2024
Heavy Duty Four-layer Steel Wire Spiral Reinforced Hydraulic Hose SAE100R9+R10+R12
NewsSep.03,2024
Heavy Duty Multi-layer Steel Wire Reinforced Hydraulic Hose SAE100R13 SAE100R15
NewsSep.03,2024
Latest Products