- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- haitian_creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- scottish-gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu

Jan . 10, 2025 12:42 Back to list
1 4 gas line
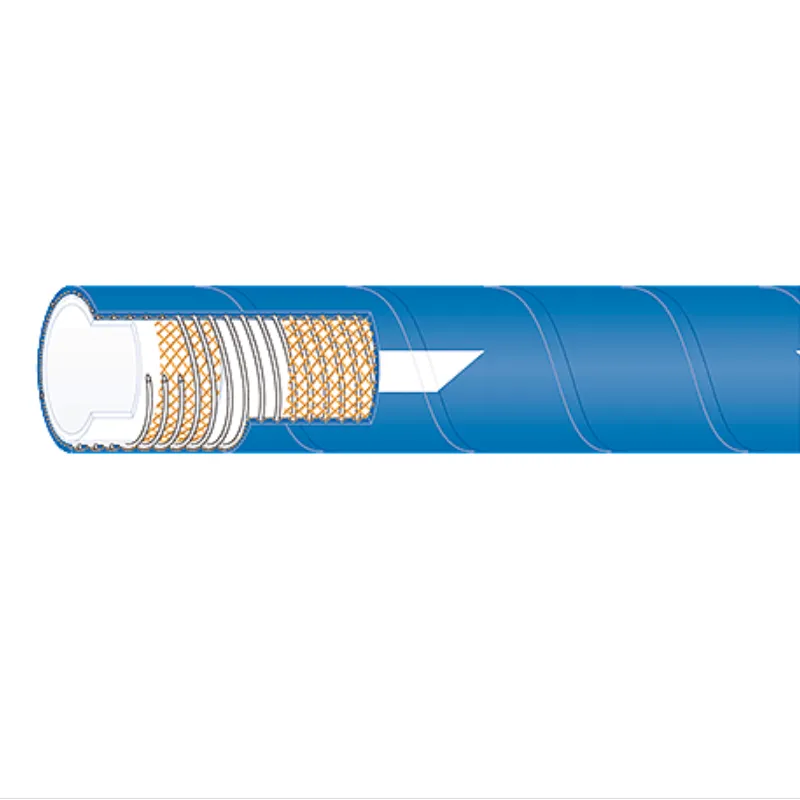

Being authoritative in this domain means upholding the industry standards set by international bodies. Compliances such as those outlined by the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) and the American Gas Association (AGA) are non-negotiable. They have extensive guidelines on diameter selection, pressure testing, and installation practices that any professional or homeowner should abide by. A meticulous analysis of these documents not only informs best practices but enforces a culture of safety. Trustworthiness doesn’t just come from certification but from demonstrated integrity and accountability in gas line installation. Professionals with a track record of transparent operations, candid disclosures about costs, potential challenges, and clear communication with clients build a reputation that precedes them. They provide insights into post-installation maintenance, recognizing that a safe installation today does not negate the possibility of issues tomorrow. Furthermore, consumers today seek products and services underlined by sustainability. Promoting environmentally safe practices, such as using recyclable materials and minimizing wastage during installation, can elevate the trust factor. The community respects and supports businesses that proactively choose eco-friendly alternatives without compromising on efficiency or safety. In conclusion, the 1 4 gas line is an integral component in a larger structural and safety narrative. For individuals seeking to understand or take on gas line installation, focusing on these elements of experience, expertise, authority, and trust can mean the difference between a robust setup and one prone to failure. By prioritizing these values, the community can enjoy the full benefits of natural gas with confidence and security.
Latest News
Steel Wire Reinforced Hydraulic Hose SAE 100 R1 / EN853 1SN S
NewsOct.17,2024
Two Layers Steel Wire Reinforced Hydraulic Hose SAE 100 R2 / EN853 2SN
NewsSep.03,2024
Textile Braid Reinforced Hydraulic Hose SAE100 R3+R6
NewsSep.03,2024
Textile Reinforced Hydraulic oil Suction Hose with embedded Steel Wire SAE 100 R4
NewsSep.03,2024
Single Wire Braid and Textile Covered Hydraulic Hose SAE 100 R5
NewsSep.03,2024
High Pressure Thermoplastic Hydraulic Hose SAE 100 R7 / EN855 R7 - SAE 100 R8 / EN855 R8
NewsSep.03,2024
Heavy Duty Four-layer Steel Wire Spiral Reinforced Hydraulic Hose SAE100R9+R10+R12
NewsSep.03,2024
Heavy Duty Multi-layer Steel Wire Reinforced Hydraulic Hose SAE100R13 SAE100R15
NewsSep.03,2024
Latest Products