- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- haitian_creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- scottish-gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu

Jan . 20, 2025 05:05 Back to list
heat resistant tubing


In aerospace, for instance, the requirements for heat-resistant tubing can be stringent, given the rapid temperature changes and high-stress conditions experienced during flight. Tubing materials here must adhere to rigorous standards to ensure reliability, as any failure could be catastrophic. Advanced materials such as titanium and high-temperature composites are often employed in this sector, reflecting the intersection of cutting-edge technology and practical application. The automotive industry similarly relies heavily on heat-resistant tubing, particularly in exhaust systems and under-hood applications where temperatures can peak dramatically. Ensuring that tubing can withstand both extreme conditions and constant vibration requires a specialized understanding of material science and engineering principles. Trust in heat-resistant tubing is built over time, rooted in consistent performance and rigorous testing. Manufacturers often subject these materials to extensive quality control tests, simulating worst-case scenarios to evaluate the reliability of their products. This process not only establishes credibility but also fortifies the user’s trust, knowing that the tubing has been thoroughly vetted for their specific application. Authoritativeness in the realm of heat-resistant tubing also stems from compliance with international standards. Adhering to guidelines such as ISO and ASTM certifications underscores a commitment to quality and safety, essential for applications where human safety and significant investments are at stake. For those looking to implement heat-resistant tubing in their operations, consulting with an expert vendor or supplier is advisable. These professionals can provide tailored insights and recommendations based on specific needs, ensuring that each component of the system works harmoniously under extreme conditions. In conclusion, heat-resistant tubing is an indispensable element across various industries, integral to maintaining safety and efficiency in high-temperature environments. With the right expertise, these tubes offer reliable solutions, underscoring the importance of informed decision-making and adherence to industry standards. By leveraging these insights, businesses can optimize their operations, safeguarding both personnel and equipment against the challenges posed by extreme heat.
Latest News
Steel Wire Reinforced Hydraulic Hose SAE 100 R1 / EN853 1SN S
NewsOct.17,2024
Two Layers Steel Wire Reinforced Hydraulic Hose SAE 100 R2 / EN853 2SN
NewsSep.03,2024
Textile Braid Reinforced Hydraulic Hose SAE100 R3+R6
NewsSep.03,2024
Textile Reinforced Hydraulic oil Suction Hose with embedded Steel Wire SAE 100 R4
NewsSep.03,2024
Single Wire Braid and Textile Covered Hydraulic Hose SAE 100 R5
NewsSep.03,2024
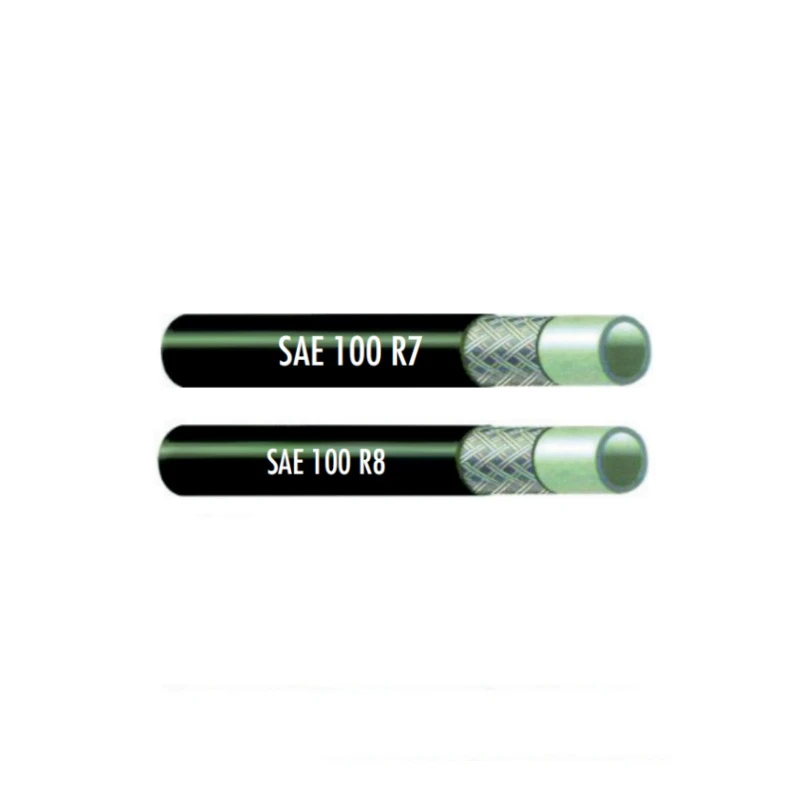
High Pressure Thermoplastic Hydraulic Hose SAE 100 R7 / EN855 R7 - SAE 100 R8 / EN855 R8
NewsSep.03,2024
Heavy Duty Four-layer Steel Wire Spiral Reinforced Hydraulic Hose SAE100R9+R10+R12
NewsSep.03,2024
Heavy Duty Multi-layer Steel Wire Reinforced Hydraulic Hose SAE100R13 SAE100R15
NewsSep.03,2024
Latest Products